What is Malware & How it is done?
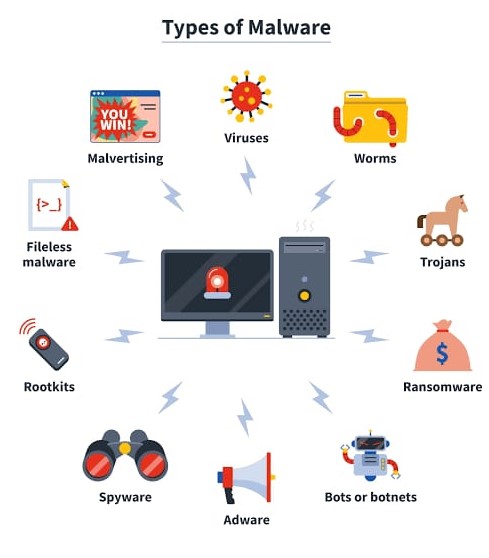
A malware attack is a type of cyber attack where malicious software (malware) is installed on a device without the owner's knowledge or consent. The malware can be used to steal sensitive information, cause damage to the device, or even spread to other devices. Common types of malware include viruses, worms, trojan horses, ransomware, and spyware. Prevention methods include keeping software up-to-date, using strong passwords, avoiding suspicious email attachments, and using antivirus software.
Process :
The process of a malware attack typically consists of the following steps:
1.Delivery: The malware is delivered to the target device through various means, such as email attachments, malicious websites, or infected software downloads.
2.Installation: Once the malware has been delivered to the target device, it may install itself either automatically or through user interaction (such as clicking on a link).
3.Execution: The malware becomes active and begins to execute its malicious code. This may include gathering sensitive information, altering or deleting files, or even infecting other devices on the same network.
4.Propagation: Some types of malware, such as worms, are designed to propagate themselves to other devices. They do this by exploiting vulnerabilities in software or networks to spread the infection.
5.Concealment: The malware may hide itself from detection by disguising itself as a legitimate file or by using rootkit techniques to evade detection.
6.Control: The attacker may use the malware to gain remote access to the infected device, allowing them to control it and carry out further attacks.
It is important to note that the process may vary depending on the specific type of malware and the attacker's objectives.
Awareness on Ransomeware for Post-production
- Employee Awareness
- Up-to-date Software
- Firewall & Antivirus
- Backup & Recovery
- Network Segmentation
- Access Control
- Regular Monitoring
Case Study :-
One real-world case study of a malware attack in a post-production company is the attack on the company Sony Pictures Entertainment in 2014. In this attack, the hackers used malware to gain access to the company's systems and steal sensitive data, including confidential emails, sensitive employee information, and unreleased films. The attackers also wiped out a large portion of the company's computer systems and threatened to release the stolen data if their demands were not met.
The investigation revealed that the attackers had used a type of malware known as a wiper, which was designed to erase data from the systems it infected. The wiper was delivered to the company's systems through a phishing email that appeared to come from a trusted source.
The attack caused significant disruption to the company's operations, with employees unable to access important systems and data for several days. The attack also resulted in the public release of confidential information and the loss of proprietary data, which caused significant damage to the company's reputation.
This case highlights the importance of taking proper precautions to prevent malware attacks, such as educating employees about cyber threats, implementing strong security measures, and regularly backing up important data. In addition, having a disaster recovery plan in place can help organizations quickly respond to a malware attack and minimize the damage caused.